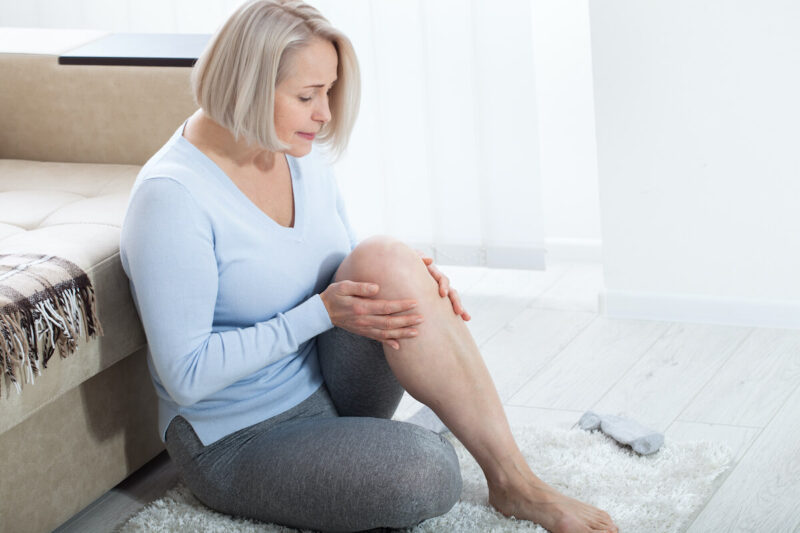
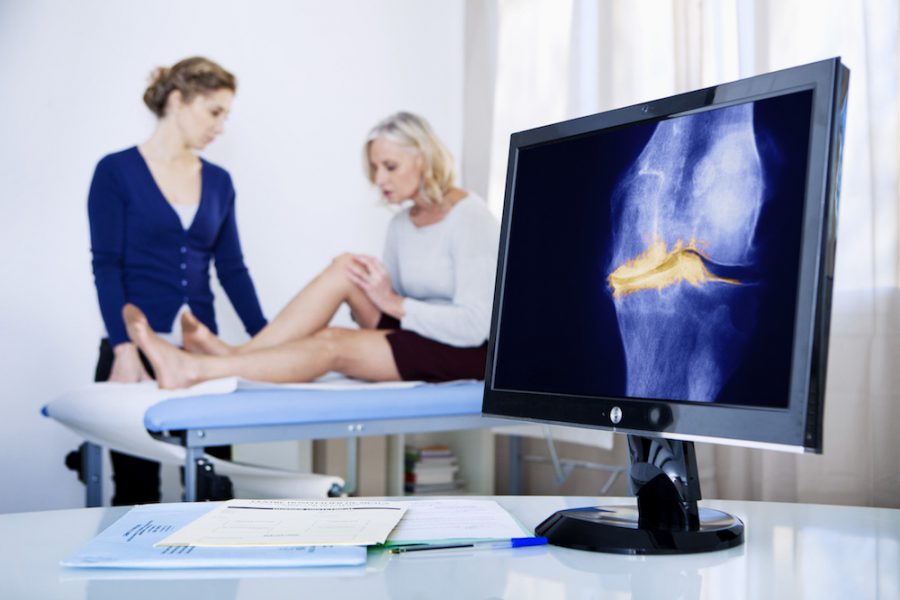
Osteoarthritis is a chronic condition that develops when cartilage between bones breaks down and wears away, causing joint pain and/or stiffness, tenderness, swelling, and loss of flexibility. Osteoarthritis may affect any joint in the body, but it is commonly observed in the hands, knees, and hips. It is the leading cause of work disability among adults in the United States and affects more than 300 million people globally, but that burden is not distributed equally. Women experience a higher overall prevalence of disease, as well as more severe symptoms and increased levels of disability.
Sex and gender disparities in osteoarthritis are more prevalent after the age of 50, at which point incidence rises sharply among women. While research suggests sex hormones as a factor that contributes to increased joint pain in women during the menopausal transition, the role of hormones is not well understood. To better understand these disparities and improve health outcomes for all, the influence of sex and gender differences must be considered in the research and clinical care for osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis is part of the SWHR Pain Network, which engages the following focus areas: Migraine and Osteoarthritis.